|

|
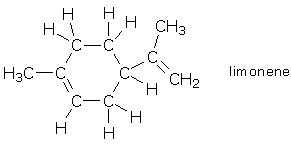
Chapter 2 - Distances Distances in a typical molecule Before we set out a bunch of rules concerning distance, let’s look at distances within a typical molecule. Perhaps we will see something that correlates with our ideas about atomic interactions and chemical bonds. Limonene is a small, yet relatively complicated hydrocarbon. You will synthesize this compound in Chemistry 202, but you probably smelled natural limonene the last time you cut open a lemon or orange. Limonene contains two kinds of atoms, carbon and hydrogen, so we will look at carbon-hydrogen and carbon-carbon distances separately. First, we observe that the 16 CH single bonds are all roughly the same length, 1.085–1.101 Å. This is an extremely narrow range, so it seems fair to say that CH bond distances generally fall around ~1.09 Å. It is tempting, though, to claim even more. Namely, we would like to say that if we ever find a C and H separated by about 1.09 Å, give or take a bit, these atoms are bonded to each other. Is this a safe statement to make? The only way to test it is to look at distances between nonbonded CH atoms and see if they fall near the critical 1.09 Å value. Looking at the nonbonded CH distances in limonene, we find that they are all much longer than 1.09 Å. C and H that are separated by a single carbon atom, as in C-C-H are separated by 2.1-2.2 Å, which is nearly twice as long as the typical “bond” distance. And, C and H that are separated by two or more carbon atoms, as in C-C-C-H, are separated by 2.6-7.8 Å, which is longer still. Therefore, CH distances can easily distinguish between bonded CH (1.08-1.11 Å), C-C-H (2.1-2.2 Å), and C-C…C-H (> 2.6 Å). Distances for other atom combinations in limonene are listed in the following table, and we find the same trends. For a given combination of atoms, XY, the XY bond is substantially shorter than the X-C-Y distance, and the latter is shorter than the X-C…C-Y distance. Since each range is quite distinct, it should even be possible to reconstruct a molecular formula from distance data alone.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||